Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation: 7 Proven Steps to Success
Implementing Oracle ERP Cloud can transform your business operations—but only if done right. Discover the 7 essential steps, common pitfalls, and expert strategies to ensure a smooth, successful transition.
Understanding Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation

Oracle ERP Cloud is a comprehensive suite of enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications delivered as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution. It integrates financials, procurement, project management, risk management, and enterprise performance management into a single, unified platform. Unlike traditional on-premise ERP systems, Oracle ERP Cloud runs on Oracle’s secure, scalable cloud infrastructure, offering faster deployment, lower IT overhead, and continuous innovation.
What Is Oracle ERP Cloud?
Oracle ERP Cloud is part of Oracle’s broader Fusion Cloud Applications suite. It replaces legacy systems with modern, AI-driven processes that automate routine tasks, improve forecasting accuracy, and enhance decision-making. The platform is designed for mid-sized to large enterprises across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and financial services.
- Core modules include Financials, Procurement, Projects, and Risk Management.
- Powered by machine learning and real-time analytics.
- Offers global compliance support for tax, legal, and regulatory standards.
According to Oracle, over 10,000 customers worldwide use Oracle ERP Cloud, including industry leaders like Nissan, FedEx, and Schneider Electric. The platform’s agility allows businesses to respond faster to market changes and scale operations efficiently.
Why Choose Cloud-Based ERP?
Moving from on-premise ERP to the cloud is more than a technology upgrade—it’s a strategic shift. Cloud ERP eliminates the need for costly hardware, reduces maintenance burdens, and enables remote access for distributed teams.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing reduces upfront capital expenditure.
- Scalability: Easily add users, modules, or regions as your business grows.
- Automatic Updates: Oracle delivers quarterly updates with new features and security patches without downtime.
“The cloud is not just a place to run your systems—it’s a platform for innovation.” — Larry Ellison, Oracle Chairman
For organizations undergoing digital transformation, Oracle ERP cloud implementation offers a future-proof foundation that supports automation, integration, and data-driven insights.
Key Benefits of Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
Organizations that successfully implement Oracle ERP Cloud report significant improvements in efficiency, visibility, and compliance. The transition isn’t just about replacing old software—it’s about unlocking new capabilities that drive competitive advantage.
Improved Financial Visibility and Control
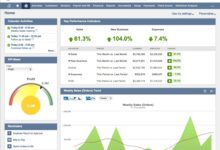
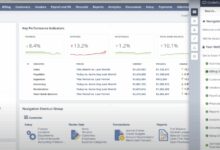
One of the most immediate benefits of Oracle ERP cloud implementation is enhanced financial reporting and control. With real-time dashboards and embedded analytics, finance teams gain instant access to cash flow, profitability, and budget performance across global entities.
- Consolidate financial data from multiple subsidiaries in minutes.
- Automate month-end close processes, reducing closing time by up to 50%.
- Enable role-based access to financial data for better governance.
For example, a multinational manufacturing firm reduced its financial close cycle from 10 days to 4 after implementing Oracle ERP Cloud. The system’s built-in compliance tools also helped them meet SOX and IFRS requirements with minimal manual intervention.
Streamlined Procurement and Supply Chain
Oracle ERP Cloud’s procurement module transforms how organizations manage suppliers, purchase orders, and inventory. It integrates seamlessly with supplier networks, enabling automated requisitioning, e-invoicing, and contract management.
- Reduce procurement cycle times by up to 40%.
- Gain real-time visibility into supplier performance and risk.
- Leverage AI-powered recommendations for optimal sourcing decisions.
A global retail chain reported a 25% reduction in procurement costs within the first year of Oracle ERP cloud implementation, thanks to better spend analytics and supplier negotiation insights.
Enhanced Decision-Making with Embedded Analytics
Oracle ERP Cloud comes with powerful analytics tools like Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) and pre-built KPIs. These allow executives and managers to monitor business performance without relying on IT for custom reports.
- Access real-time dashboards for revenue, margins, and project profitability.
- Use predictive analytics to forecast cash flow and demand.
- Drill down into transaction-level data with a few clicks.
Unlike legacy systems that require data extraction and manual reporting, Oracle ERP Cloud delivers insights directly within the application. This empowers faster, more accurate decision-making across departments.
Common Challenges in Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
Despite its many advantages, Oracle ERP cloud implementation is not without challenges. Organizations often underestimate the complexity of data migration, change management, and process reengineering. Understanding these hurdles upfront can help mitigate risks and ensure a smoother rollout.
Data Migration and Integration Issues
Migrating data from legacy systems is one of the most critical—and risky—phases of Oracle ERP cloud implementation. Incomplete, inconsistent, or poorly formatted data can lead to system errors, reporting inaccuracies, and user frustration.
- Legacy systems often contain redundant or outdated records that must be cleansed before migration.
- Mapping data fields between old and new systems requires deep technical and business knowledge.
- Integration with third-party systems (e.g., CRM, HRIS) must be carefully planned and tested.
According to a 2023 Gartner report, 60% of ERP implementation failures are linked to poor data quality. To avoid this, organizations should conduct a thorough data audit and use Oracle’s Data Migration Workbench to streamline the process.
User Resistance and Change Management
Even the most advanced ERP system will fail if employees resist using it. Change management is often overlooked, yet it’s crucial for user adoption and long-term success.
- Employees may fear job displacement or struggle with new workflows.
- Lack of training leads to low productivity and increased errors.
- Without executive sponsorship, teams may revert to old systems or spreadsheets.
A successful Oracle ERP cloud implementation requires a structured change management plan that includes communication, training, and continuous support. Involving key users early in the design phase can also increase buy-in and reduce resistance.
Scope Creep and Project Delays
Many Oracle ERP cloud implementation projects go over budget or miss deadlines due to scope creep—adding new features or customizations mid-project. While customization may seem beneficial, it can delay go-live, increase costs, and complicate future upgrades.
- Stakeholders often request additional reports, workflows, or integrations after the project starts.
- Lack of clear governance leads to conflicting priorities and decision paralysis.
- Unrealistic timelines fail to account for testing, training, and user feedback cycles.
To avoid delays, organizations should define a clear project scope during the discovery phase and establish a change control board to evaluate any new requests. Oracle’s Rapid Implementation methodology can help keep projects on track with pre-built templates and best practices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
A successful Oracle ERP cloud implementation follows a structured methodology. While Oracle provides its own implementation framework, organizations can adapt it to their specific needs. The following seven-step approach ensures clarity, control, and continuity throughout the process.
Step 1: Define Business Objectives and Scope
Before any technical work begins, stakeholders must align on the goals of the Oracle ERP cloud implementation. Is the primary objective cost reduction, compliance, scalability, or operational efficiency?
- Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
- Determine which modules (e.g., Financials, Procurement) will be implemented.
- Define the rollout strategy: phased (by module or region) or big bang (all at once).
Engage executives, finance leaders, IT, and process owners in workshops to gather requirements and prioritize needs. Document the scope in a formal project charter to prevent scope creep later.
Step 2: Assemble the Right Implementation Team
Oracle ERP cloud implementation requires a cross-functional team with diverse skills. Relying solely on IT or external consultants is a common mistake.
- Include business process owners who understand day-to-day operations.
- Assign a dedicated project manager with ERP experience.
- Engage Oracle partners or certified consultants for technical expertise.
Oracle recommends using its PartnerNetwork to find qualified implementation partners. Firms like Deloitte, Accenture, and Capgemini have deep expertise in Oracle ERP Cloud deployments.
Step 3: Conduct a Current-State Assessment
Understanding your existing processes is essential for designing an effective future state. A current-state assessment identifies inefficiencies, redundancies, and compliance gaps in your legacy systems.
- Map existing workflows for finance, procurement, and project management.
- Document pain points and user feedback from current ERP or spreadsheet usage.
- Evaluate data quality and integration points with other systems.
This assessment serves as a baseline for measuring improvement post-implementation. It also helps identify which Oracle best practices can be adopted versus customized.
Step 4: Design the Future-State Solution
With a clear understanding of current processes, the team can design the target operating model. Oracle ERP Cloud is built on industry best practices, so the goal is to align business needs with standard functionality whenever possible.
- Configure chart of accounts, ledgers, and organizational structures.
- Design approval workflows, budget controls, and procurement policies.
- Plan integrations with existing systems using Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC).
Use Oracle’s Fusion Cloud Documentation to understand configuration options and limitations. Avoid excessive customization to ensure easier upgrades and lower maintenance costs.
Step 5: Execute Data Migration and Testing
Data migration is a make-or-break phase. It involves extracting data from legacy systems, transforming it to fit Oracle’s data model, and loading it into the cloud environment.
- Use Oracle’s Data Migration Workbench for structured, repeatable migrations.
- Perform multiple test migrations to validate accuracy and performance.
- Conduct end-to-end testing with real-world scenarios, including month-end close and invoice processing.
Testing should involve super users from each department. Oracle’s Application Testing Suite can automate regression testing to ensure system stability after updates.
Step 6: Train Users and Prepare for Go-Live
No matter how well the system is configured, user adoption depends on effective training and support. A well-trained workforce is more confident, productive, and less likely to make errors.
- Develop role-based training programs (e.g., for accountants, buyers, project managers).
- Use Oracle’s Oracle University for certified courses and e-learning modules.
- Create quick-reference guides, video tutorials, and FAQs for ongoing support.
Conduct a dress rehearsal or mock go-live to simulate real operations. Address any issues before the actual cutover date.
Step 7: Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support
The go-live phase marks the official transition from old to new systems. However, the work doesn’t end there. Post-implementation support is critical to address user issues, optimize performance, and drive continuous improvement.
- Establish a help desk or support team available during peak hours.
- Monitor system performance and user feedback for the first 90 days.
- Schedule regular reviews to identify process improvements and additional training needs.
Oracle offers Cloud Customer Connect and support services to assist with troubleshooting and best practice guidance after go-live.
Best Practices for a Successful Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
While every implementation is unique, certain best practices consistently lead to better outcomes. These strategies help organizations avoid common pitfalls and maximize the value of their investment.
Adopt Oracle’s Rapid Implementation Methodology
Oracle provides a structured approach called Rapid Implementation, designed to accelerate deployment using pre-built configurations, data templates, and implementation playbooks.
- Reduces implementation time by up to 40% compared to traditional methods.
- Includes pre-configured setups for common industries and regions.
- Enables parallel workstreams for faster execution.
By leveraging Oracle’s standard templates, organizations can minimize customization and focus on business outcomes rather than technical setup.
Leverage Oracle’s Cloud Platform Services
Oracle ERP Cloud doesn’t operate in isolation. It integrates with other Oracle Cloud services like Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC), Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC), and Oracle Identity Management.
- Use OIC to connect ERP with CRM, HR, and supply chain systems.
- Deploy OAC for advanced reporting and predictive analytics.
- Ensure secure access with Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS).
These services enhance functionality without requiring custom coding, making the Oracle ERP cloud implementation more robust and scalable.
Focus on Continuous Improvement
ERP implementation is not a one-time project—it’s the beginning of a continuous improvement journey. Oracle delivers quarterly updates with new features, so organizations must stay agile.
- Assign a center of excellence (CoE) to manage ongoing enhancements.
- Monitor user feedback and system performance metrics regularly.
- Plan for periodic process optimization and module expansion.
Companies that treat Oracle ERP Cloud as a living system—not a static tool—achieve the highest return on investment.
Real-World Case Studies of Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
Learning from real-world examples can provide valuable insights into what works—and what doesn’t—during Oracle ERP cloud implementation.
Nissan Motor Corporation
Nissan implemented Oracle ERP Cloud across 150+ countries to standardize financial processes and improve global visibility. The project replaced over 200 legacy systems with a single, unified platform.
- Reduced financial close time from 10 days to 5.
- Improved compliance with local tax regulations in each region.
- Enabled real-time reporting for executive decision-making.
The success was attributed to strong executive sponsorship, a phased rollout, and extensive user training.
Schneider Electric
Global energy management leader Schneider Electric used Oracle ERP Cloud to streamline procurement and financial operations. The implementation supported their digital transformation strategy.
- Automated 80% of purchase order processing.
- Reduced invoice processing time by 60%.
- Integrated with supplier networks for real-time collaboration.
By adopting Oracle’s best practices and minimizing customization, Schneider achieved a faster time-to-value.
FedEx
FedEx implemented Oracle ERP Cloud to enhance financial planning and reporting across its logistics network. The system supports complex revenue recognition and multi-currency transactions.
- Improved forecast accuracy with AI-driven analytics.
- Centralized financial data from 220+ countries.
- Reduced manual journal entries by 70%.
The project emphasized data governance and change management, ensuring high user adoption.
Future Trends in Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation
As technology evolves, so does Oracle ERP Cloud. Organizations planning an implementation should consider emerging trends that will shape the future of ERP.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Oracle is embedding artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into ERP processes to automate routine tasks and provide intelligent insights.
- AI-powered assistants can answer natural language queries (e.g., “What’s our cash position?”).
- ML algorithms detect anomalies in financial transactions for fraud prevention.
- Predictive forecasting improves budgeting and demand planning.
Future Oracle ERP cloud implementation projects will increasingly leverage these capabilities to drive efficiency and innovation.
Increased Focus on User Experience (UX)
Modern users expect intuitive, mobile-friendly interfaces. Oracle has invested heavily in improving the UX of its cloud applications.
- Responsive design allows access from smartphones and tablets.
- Personalized dashboards adapt to user roles and preferences.
- Voice-enabled navigation is being tested in pilot programs.
Organizations should prioritize UX during implementation to boost adoption and satisfaction.
Expansion of Ecosystem Integrations
Oracle is expanding its integration ecosystem through partnerships and APIs. Future implementations will benefit from seamless connections with third-party apps like Salesforce, Slack, and Microsoft Teams.
- Use Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) to build custom workflows.
- Leverage pre-built adapters for popular SaaS applications.
- Enable real-time data sync across platforms.
These integrations make Oracle ERP Cloud a central hub for enterprise operations.
What is Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation?
Oracle ERP Cloud Implementation is the process of deploying Oracle’s cloud-based ERP system to manage financials, procurement, projects, and risk. It involves planning, data migration, configuration, testing, training, and go-live support to replace legacy systems with a modern, scalable solution.
How long does Oracle ERP Cloud implementation take?
Implementation timelines vary based on complexity, but typically range from 6 to 12 months. Rapid Implementation projects can go live in as little as 3-4 months using pre-built templates and best practices.
What are the main challenges in Oracle ERP cloud implementation?
Common challenges include data migration issues, user resistance, scope creep, and integration complexity. Success requires strong project management, change management, and stakeholder alignment.
Can Oracle ERP Cloud be customized?
Yes, but Oracle recommends minimizing customization to maintain upgradeability. Most business needs can be met using configuration options, workflows, and Oracle’s extension framework.
Is Oracle ERP Cloud secure?
Yes. Oracle ERP Cloud runs on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), which offers advanced security features including encryption, identity management, threat detection, and compliance certifications (e.g., GDPR, SOC 1/2).
Oracle ERP cloud implementation is a transformative journey that can modernize finance, streamline operations, and empower data-driven decisions. By following a structured approach, leveraging best practices, and learning from real-world examples, organizations can achieve a successful deployment. The key is to focus not just on technology, but on people, processes, and continuous improvement. With the right strategy, Oracle ERP Cloud becomes more than a system—it becomes a strategic asset.
oracle erp cloud implementation – Oracle erp cloud implementation menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: